Introduction to Blockchain for Businesses
It’s important to know what blockchain technology is and how it might affect your business. Within two or three years, your vendors may implement blockchain distributed-ledger technology (DLT). It will affect the way you are charged and pay for your services, and your vendors may require you to use it.
The concept of blockchain technology first appeared in 1982 academic papers but wasn’t put into real-world use until 2009 with the introduction of Bitcoin. Blockchain worked its way into our lexicon as part of the buzz around Bitcoin. Blockchain has evolved since 2009, and companies are beginning to use it for different applications. In the future, this technology will likely play a role in legal contracts, medical records and a vast number of other recordkeeping needs.
In fact blockchain technology is expected to transform entire industries. According to Insider Intelligence, “Global spending on blockchain is forecast to reach nearly $17.9 billion in 2024, growing at a five-year compound annual growth rate of 46.4%.”
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a cloud-based, decentralized technological solution that establishes a permanently linked chain of digital assets and information. Records of information are established in an encrypted block of data. As other blocks are added, they form a chain. The blockchain captures each transaction at the moment in time that it was created and protects it. Everyone has access to the same information from anywhere in the world, as long as they have the computing power to participate.
Records that are recorded in the blockchain are permanent, irreversible and therefore indisputable. Members of a blockchain work within protocols that serve as a centralized form of governance over the records. Randomly generated algorithms, cryptographic keys and signatures make the chain unbreakable and protect the data from hackers and corruption.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Using distributed ledger technology (DLT), blockchain allows individuals to work together directly to make secure transactions without the involvement of a third-party intermediary such as a bank or government entity. Each transaction record creates a time-stamped “block” within the chain and is cryptographically linked to previous blocks.
A block cannot be changed once it has been added to the chain, and each new block must be independently verified by peer-to-peer (P2P) computer networks. Each computer is considered a “node” on the blockchain. The nodes are connected and stay up to date by exchanging the latest blockchain data. Each node contains a full copy of the transaction history of the blockchain. This creates the distributed ledger that is not centrally housed as a traditional database would be. Every node in the blockchain has access to the ledger, and no one person has administrative rights.
The graphic below illustrates the blockchain technology process:
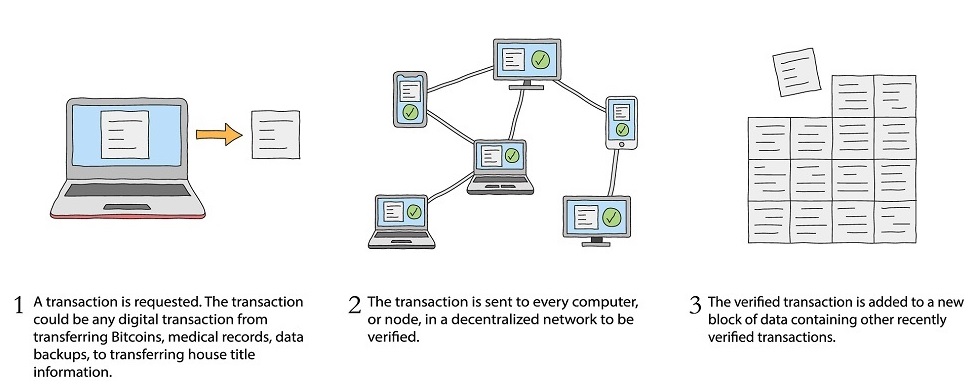
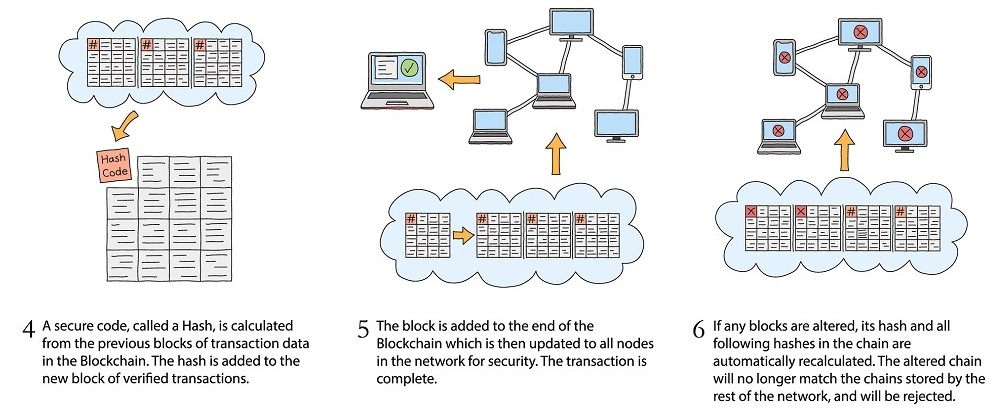
You might think about blockchain technology as a Google spreadsheet that is strongly encrypted and verified. Each entry on the document depends on a logical relationship to all its predecessors and is agreed upon by everyone in the network. Because everyone in a blockchain has access to the same digital ledger with the same information, there is continuous transparency and reconciliation. Nothing can be added to the ledger without the consent of everyone in the blockchain.
There is no centralized version that hackers can attack, and you don’t need a bank or other trusted third party to verify information and transactions. The chain is considered hack-proof, because it is stored across a network of computers. Nothing can change without the permission of all the participants. The records cannot be altered and are encrypted from one end to the other. Processing transactions with blockchain can be more time and cost-efficient. too. Manual tasks are reduced, audits and reporting are easier, and there’s no middleman to pay.
How is Blockchain Used?
A major benefit of blockchain is the trust its members are able to share. Blockchain enables an ecosystem of shared data with no one player in charge. The principles of blockchain replace the trust that a third party would normally bring to the transaction. With blockchain, businesses no longer need the third party to introduce partners and guide the process. This allows business dealings to grow and evolve on their own without unnecessary fees and payments. The involved parties can track everything from complex shipping logistics to complicated telecommunications network transactions and widely distributed supply chain components.
Consider the supply chain that aggregates fruits and vegetables from all over the world, starting with the source farm or orchard and ending on your neighborhood grocery store shelves. With widespread suppliers and shipping logistics, it can be hard to trust every entity along the supply path. Blockchain builds that trust with its immutable transaction records and shared permission system. When a food item is recalled, distributors can use the block chain to trace a food step by step back to its specific source. It can allow a company to continue shipping other produce while cutting off the contaminated supply stream.
Drawbacks to Blockchain?
Certain processes are better suited to blockchain than others. Businesses that conduct extensive transactions such as financial and healthcare institutions have used blockchain to streamline and improve processing and record-keeping. There are some caveats to consider, however.
If your business wants to switch some of its practices and implement blockchain-based applications, it needs to manage the change from existing processes and prepare for the investments in technology. Blockchain requires the assumption that everyone involved will stick to proscribed standards. Even though the technology is decentralized, there needs to be some form of oversight—whether it’s artificial intelligence, another system or people—to confirm information.
While blockchain has the potential to disrupt traditional business practices, some of the things that make it unique and useful can also prove to be a disadvantage. As blockchains grows larger, it may become more challenging to coordinate node-wide approvals. Because the chain is distributed across a broad network of decentralized computers, it requires more equipment and more computing power. This increases monetary investment and limits scalability.
Another drawback is that extensive use of blockchains require excessive electricity to power all the necessary computations that encrypt the chain as it passes back and forth to each user gathering permissions. Not only does this add expense, but it can cause negative environmental impact.
Not every company will be able to justify the cost in time and money, especially if the return is limited in their case. Blockchain can add complexity where it may not be needed. But in certain situations, blockchain fills a need and is expected to disrupt and transform how businesses operate.
Looking Forward
No matter how you look at it, blockchain is here and will affect how you conduct business going forward. The technology is still in its early days, and there is much to explore and resolve.
Sage Management, an affiliate company to Cost Control Associates, has been working with blockchain solutions since the technology’s inception. Sage partners with international organizations establishing global blockchain standards and are recognized experts in the field. They use their extensive in-house knowledge to serve clients who are considering or preparing for a blockchain solution. To learn more, contact us.
