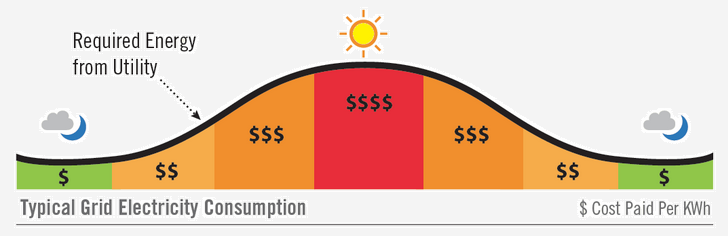
Energy providers have an interesting problem: They are required by law to produce enough energy to meet peak usage for their total customer base, independent of time of day or season. This includes all residential, businesses, government facilities and school districts in their coverage area. The problem is that energy usage generally reaches peak capacity for a few hours a day, if at all. Peak usage can vary widely by season and affects different types of consumers differently.
By requiring a baseline of energy production, energy producers generally lose money to overproduction during non-peak periods. This inefficiency, in the form of additional production costs, is typically passed on to consumers using energy during peak hours.
Fortunately, there is often a little known solution to this situation for energy consumers. Many utility companies offer alternative rate structures, often referred to as Time-of-Use (TOU) rates.
What are Time-of-Use Rates?
Time-of-Use (TOU) rates are alternative rates for energy used during off-peak hours that are lower than what is charged under standard tariff rates. Under a TOU rate structure, a consumer is not only billed for the energy they use, but also when they use it.
TOU rates reward energy consumers which have long operating hours or facilities that consume similar amounts of energy in off-peak hours as in peak hours. These might include manufacturers, multi-location franchises or retailers, as well as, certain government facilities. By switching to a TOU rate structure these consumers can offset higher peak energy costs with savings derived from lower costs during off-peak hours.
In many cases, if the facility has long operating hours, little or no adjustment in operations are needed in order to benefit from these rates. However, a happy coincidence of switching to alternative rate structures is often an increased awareness of consumption patterns, opening up opportunity to increase efficiency in the long run.
When to Take Advantage of Time of Use Rates?
TOU Rates vary by state and energy provider. In states like Arizona and California, TOU rates are typically quite lucrative for large energy consumers. If you consume a large amount of energy in off-peak hours, TOU rates will generally result in cost reductions, no matter where you’re located.
Off-peak hours include nights, weekends and holidays. The types of customers ideally suited to take advantage of TOU rates are typically municipalities, city or state governments that provide services around the clock and 7 days a week, such as:
- Water Filtration
- Sewage Pump Stations
- Police Department/Jail
- Fire Department
Similarly, large multi-location retailers open on weeknights and weekends should benefit from TOU rate structures.
Missed Opportunity
In many cases we have found that businesses, municipalities and school districts are not taking advantage of time-of-use rates, and a number of other potentially lucrative alternative and special rates. These large energy consumers are missing serious savings, often tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars per year, depending on consumption.
In some states, certain utility providers have done away with TOU rates because consumers have failed to take advantage of the rates.
Time-of-Use Rates are a win-win for utilities and their customers. Utilities recover some of the costs from required over-production in non-peak hours and their customers decrease energy costs by taking advantage of more appropriate rating structures. In the end everyone reduces expenses and wins.
Think you might be able to take advantage of Time-of-Use Rates?
We can help you find out if alternative rate structures can help you, and exactly how much you can save. Please call Keith Laake at 518-798-4437 with questions or to learn more.